Gone are the times when the Risk Management Department’s role was one of “compliance” with obligations to provide information. The ongoing Covid-19 pandemic and climate change are revealing the complexity and potential fragility of the market contexts in which we, like many others, are called upon to operate.
Risk Management’s responsibility is involving an increasing capacity to provide forecasts, describe future scenarios in both the short-term, to identify and mitigate contingent risk for business operations, and long-term, to support strategic decision making and identify new opportunities.
Artificial Intelligence and High-Frequency Data
Describing the future by modelling scenarios, anticipating structural changes caused by variables (such as keenness to travel, smart working, ticket prices, the ageing of the population, propensity to consume, consumers’ concern about sustainability and “healthy” eating) all become dimensions that must inform business strategy, now more than ever at the mercy of the risk vs opportunity dilemma: foreseeing risks sufficiently early becomes an essential competitive advantage.
This is why the new Risk Management Department, created in 2020, annus horribilis, employs the capabilities and instruments of the new “Data Science”: non-conventional high-frequency data, monitoring of social networks, exogenous variables that come together and correlate with the quantitative dimensions specific to the business (traffic vs. sales), machine learning, stochastic simulation.
A set of highly powerful analytical “weapons” harnessed to the robust and now mature practices of risk management, such as periodical measurement of endogenous operating risk and financial impact risks, make ERM a valuable tool supporting the work of the management and board of directors.
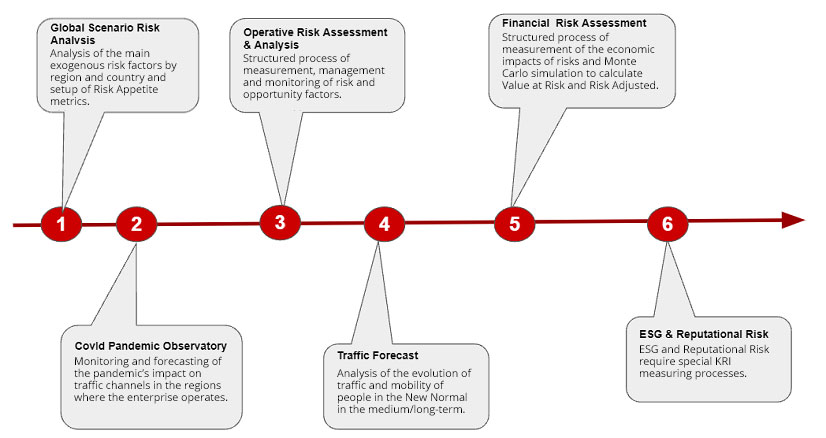
The Customer’s Voice, Sustainability and Reputational Risk
ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) is a huge opportunity for change in businesses and requires a new focus on (and specific metrics for) aspects that were once ancillary to business processes and have now become central: investment in diversity, equal opportunities, non-discrimination of employees, inclusion, environmental sensibility, use of renewable energy sources, responsible use of potentially depleting resources (eg. water) and reducing processing waste. Business is undergoing a deep transformation that needs to be strictly governed in terms of methods, practices, responsibilities and policies and that requires new measurable indicators (KPI) and new delta values with respect to such indicators as a measure of risk (KRI: Key ESG Risk Indicator).
Other fronts include digitalization and the ecosystem of customers, net promoters, people who believe in and support the Autogrill brand and recognize value in our corporate identity but can also be critical and join with others using the sounding board of social networks, which heightens reputational risk.
These are all new risk-opportunity dimensions generated by ever accelerating modernity and which we handle, here in Autogrill’s Risk Management Department, with corresponding modernity: monitoring social networks, measurement of the customers’ voice and its “colour”, travellers’ mood (trust, fear, happiness, anger…) using the methods of Machine Learning and quantitative risk analysis.
Risk Appetite and Risk Reward
In the Risk Management Department, we believe that risk is basically a friend of business. If there’s no risk, there’s probably little or no opportunity.
Modern Risk Management methodology prefers to talk about the trade-off between risk and opportunity in quantitative terms using the new categories and new metrics of Risk Appetite.
Like financial investments, many business decisions involve a reward in a situation of uncertainty. We talk about “expected reward” in a statistical sense and with respect to the uncertainty or volatility of the result of a given business decision (such as deciding to invest in an emerging market).
Here too, Risk Management employs new methods and frameworks to more effectively support strategic decisions, such as optimizing the investments portfolio against risk that’s acceptable to the business (Risk Appetite) and measured by a maximum volatility of return on investment, a process that requires and confirms integration of the risk assessment activities within business processes.
On track for an Extremely Challenging Future
The world is changing and offering enterprises new challenges and new opportunities in a more complex and volatile general context to which the ERM Department responds with modern tools like the new “Data Science”, high-frequency data, monitoring social networks and stochastic simulation. However, the key factor for the success of Risk Management remains the level of informed participation in risk assessment on the part of business owners and managements, i.e. the maturity of an organization and its organizational model.
"The entire organization must contribute proactively to risk management and not just the people assigned to the task. What our risk management model offers is integration within the organizational setup as a whole."
Risk Management has thus shown itself to be a central function providing risk management methodology and support for the Group’s regional managements and offering the board of directors an instrument for gauging the acceptability of the level of risk taken, compatibly with the achievement of its business objectives.
October 19, 2021

